How to Master Google Ads Targeting: Basics and Strategies for Success
2024-07-14

Showing your Google ads to the right people is essential for making the most of your budget, as we’ve talked about in our article about Google ads costs.
Now, we will dive a bit deeper into the topic and walk you through the different Google Ads targeting options, offering practical tips to help you connect with your ideal customers.
Why you should pay attention to your targeting options
Before we talk about specific targeting options available for Google ads, let’s list some reasons why you should take targeting seriously:
- Making the most of your money: when you aim your ads at the right people, you're not wasting money on clicks from folks who aren't interested. This means your advertising budget goes further and you get a higher ROAS;
- Getting more customers: when your ads reach people who are already interested in what you offer, they're more likely to become customers. It's like talking directly to the people who want what you've got – you don’t have to do a lot of convincing;
- Getting your name out there: when you target the right audience, more people who are likely to buy from you see your ads. This builds awareness of your brand among the right people and can lead to more sales in the future;
- Improving your ads over time: by learning about your audience and how they respond to your ads, you can tweak things to make your campaigns even more effective. This way, you can get better results with every ad you run;
- Standing out from the competition: when you know who your audience is, you can tailor your ads to grab their attention. This helps you beat out competitors and attract customers who are looking for exactly what you offer.
As you can see, there are many benefits to spending time researching various targeting options and choosing the ones most suitable for your campaigns. Basically, this can influence the outcomes of your campaigns both in the short and long term, so you definitely want to get this right.
Types of Google ads targeting
Google provides you with multiple targeting options to reach the right people, and this quantity can seem a bit confusing at first.
However, we can break all of these options down into two main categories: audience targeting and content targeting.
1. Audience targeting
Audience targeting in Google Ads means showing your ads to specific groups based on their characteristics and online behavior. There are several ways to do so:
Demographic targeting
Demographic targeting lets you target people based on their age, gender, income, whether they have kids or not, and so on. This helps you tailor your ad campaigns to match the interests and needs specific groups of people can share in common based on more objective and stable characteristics (e.g. compared to interests).
For example, if you sell high-end clothes, you can target affluent individuals in their 30s to 50s who are more likely to appreciate luxury products. If you sell something cheaper that is likely to appeal to different groups of people, you can broaden your targeting to reach more people.
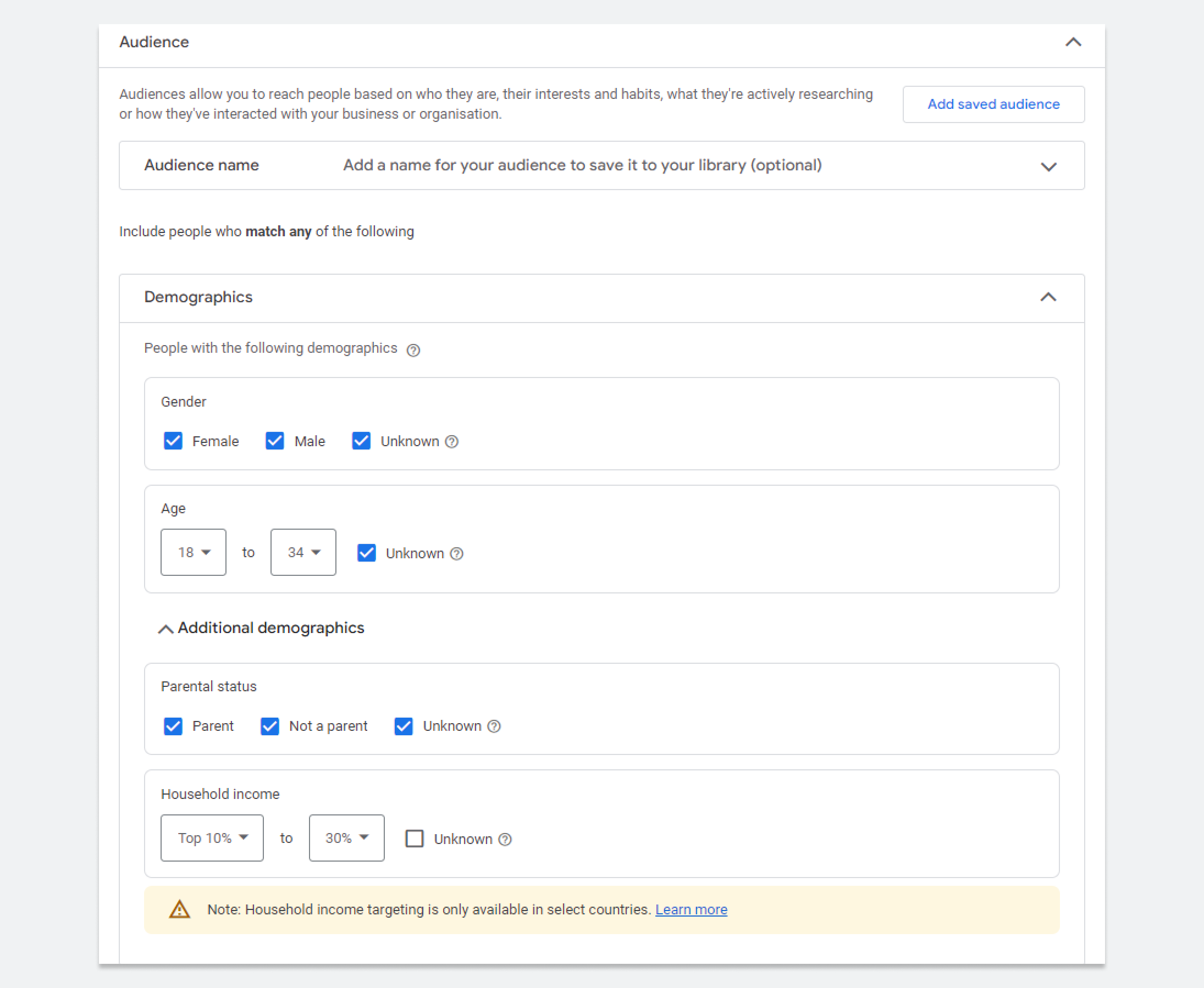
You can select age, gender, parental status, and household income in the demographic targeting section.
However, demographic targeting can sometimes be too rigid. It might miss potential customers who don't fit into typical categories but could still be interested in what you offer. For example, by focusing only on older customers based on your assumption that it’s your primary category of paying customers, you might miss out on targeting younger people who are enthusiastic about luxury items.
So, don't make your demographic targeting too narrow unless you’re running ads tailored specifically to this group of people.
If you narrow it down too much, you might miss out on customers who don’t fit perfectly into specific categories but would still be interested in what you offer. To avoid this, keep an eye on your campaign performance and tweak your demographic settings based on what you see.
Interest targeting
Interest targeting lets you show ads to people based on their hobbies, habits, passions, and other psychographic characteristics. There are two kinds of interest targeting on Google:
1. Affinity segments
Affinity segments are great for connecting with people who have long-term interests that match your business. As Google provides plenty of options, you’ll definitely find something that fits your campaigns.
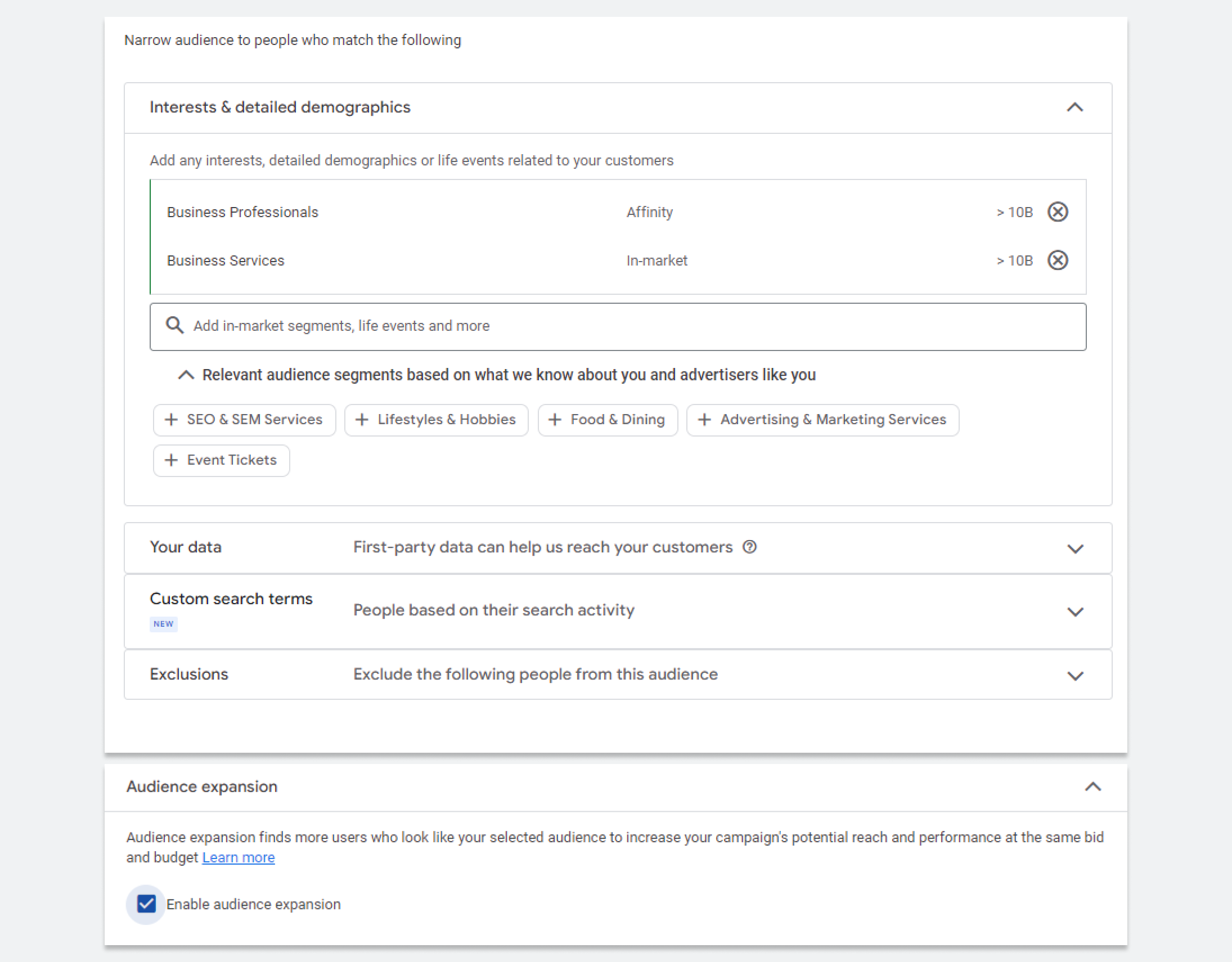
You can select different Affinity and In-market segments, use your own data segments (in other words, create custom audiences), target people based on their search activity, exclude certain users fro your audience, and a lot more.
This kind of targeting is great for building brand awareness among groups that are really into specific topics and hobbies. By tapping into their passions, you can connect with an audience that is more likely to engage with your ads and become loyal.
2. In-Market segments
This option helps you focus on people who are actively looking to buy products or services similar to what you offer.
This approach can help you increase conversions because you're reaching customers who are already interested in making a purchase decision. For example, if you provide SEO services, targeting users who are actively searching for "SEO services" ensures that your ads appear at the moment when they're most likely to decide to hire someone like you. This way, you're more likely to convert those users into actual clients or customers.
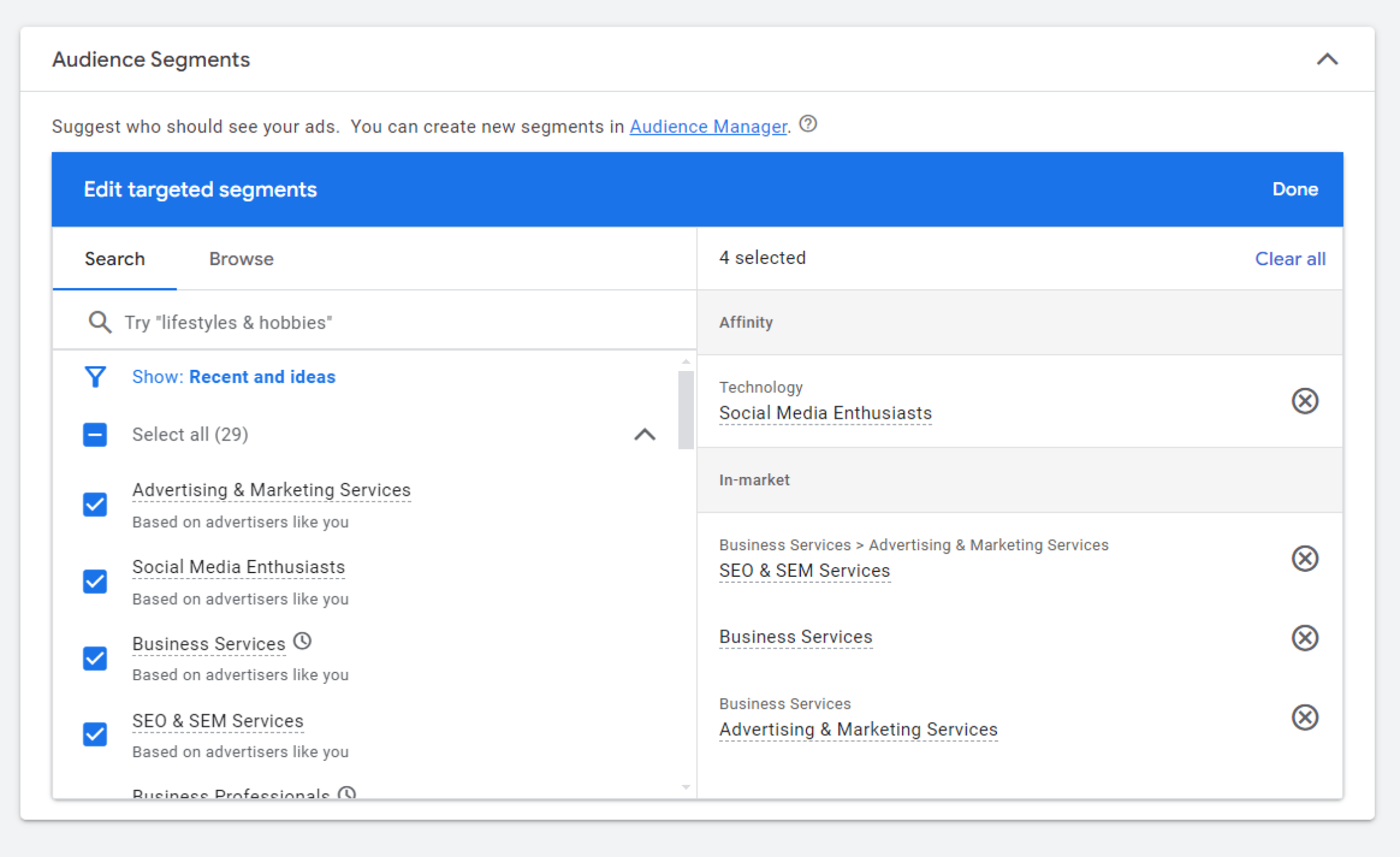
Besides looking for already existing Affinity and In-market segments, you can also create your own in Audience Manager.
Targeting users based on their interests, whether through affinity or in-market audiences, can improve how well your ads work. This is especially true when you have an audience that is diverse in terms of demographics, but you still want to narrow it down.
But you have to keep in mind that affinity segments can sometimes be too general and include users who might not be at the stage of the sales funnel where they’re close to converting.
Meanwhile, in-market audiences can be more expensive and competitive, especially when lots of advertisers are targeting the same groups of potential customers.
The key to using interest targeting correctly is understanding what stages of the sales funnel you want to reach (e.g. those who don’t even know about your business yet vs. those who are ready to explore your offers) and getting your priorities straight.
Remarketing
Remarketing allows you to re-engage with people who have already visited your website, used your app, or interacted with your YouTube channel.
Since these users are already familiar with your brand, remarketing campaigns can have higher conversion rates and a better return on investment (ROI). For example, showing ads to users who abandoned their shopping cart can remind them to come back and complete their purchase.
However, to run effective remarketing campaigns, you need a decent amount of traffic on your website. If your site doesn't attract enough visitors, your remarketing efforts might not be as effective. And remember that it's essential to manage your remarketing strategy carefully to avoid bombarding people with your ads after they make their final decision.
Also, when there’s enough data in your remarketing lists that Google can use, it will create similar segments or lookalikes which include groups of users who have online behavior similar to those you’re already targeting. These new users are more likely to be interested in your products or services.
2. Content targeting
This targeting option lets you choose where your ads will show up based on the websites, apps, videos, or specific placements you select. Instead of targeting people by who they are or what they're searching for, you target them based on the content they're already interested in. This way, your ads appear in places where your audience is most likely to see them and engage with them.
There are three main methods of content targeting:
Keyword targeting
Keyword targeting makes sure your ads show up on websites and pages that match the keywords you select. This way, you can connect with people who are already interested in what you offer.
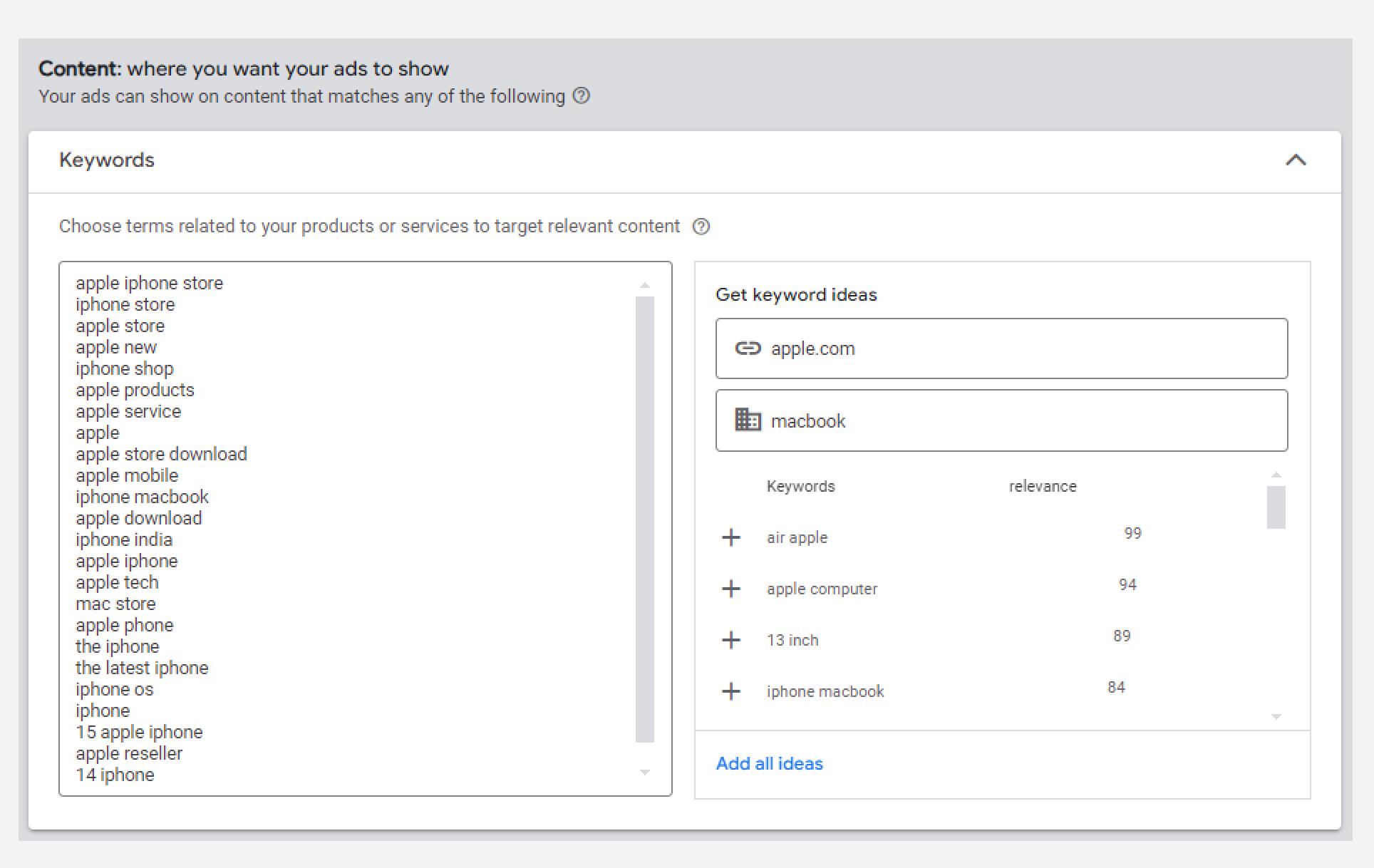
You can find relevant keywords based on your website or the product you're selling.
For example, if you sell hiking gear and target keywords like "best hiking trails", your ads will be seen by users actively searching for hiking information or products.
But remember: it's important to keep an eye on your keywords regularly because trends and how people search can change over time. Plus, managing your budget wisely is crucial, especially with popular keywords that can be costly. If you want more insights about Google ads keywords and how they work, check out the article we’ve written before.
Topic targeting
Topic targeting allows you to show your ads on websites and pages that cover specific subjects related to your business. So, instead of relying on specific keywords, you can reach a broader audience interested in certain topics. For example, if you target topics like "healthy recipes", your ads will appear on pages about cooking, reaching users who are interested in healthy eating habits.
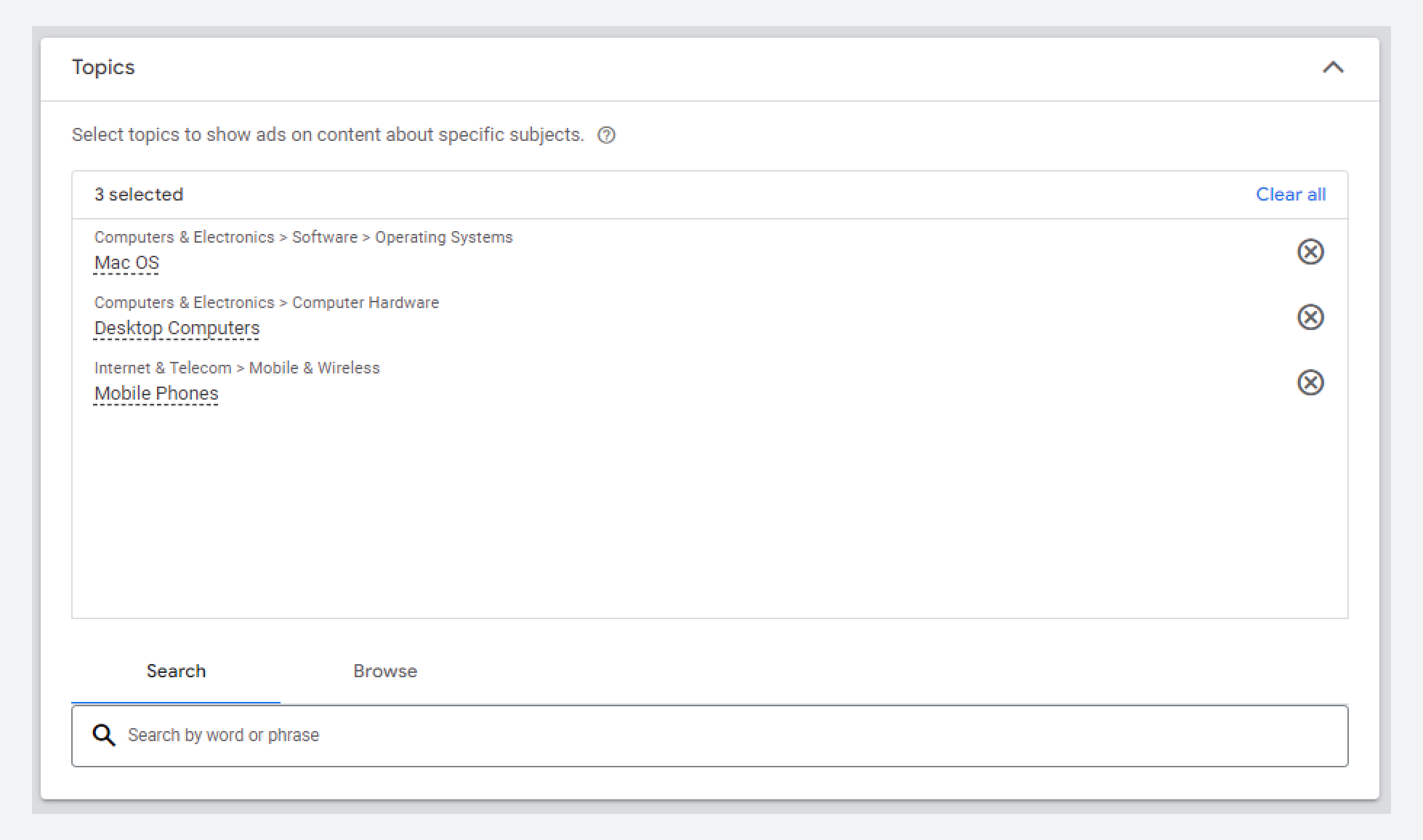
You can find relevant topics for targeting your Google ads based on specific words or phrases.
That being said, topic targeting may not be as precise as keyword targeting. Ads placed based on topics alone can reach users with different interests within the same category, which might lower conversion rates. To make your ads relevant, you'll need to create compelling ad copy and visuals.
Placement targeting
Placement targeting gives you control over where your ads appear by allowing you to select specific websites or apps. This ensures your ads show up alongside content that aligns with your brand values.
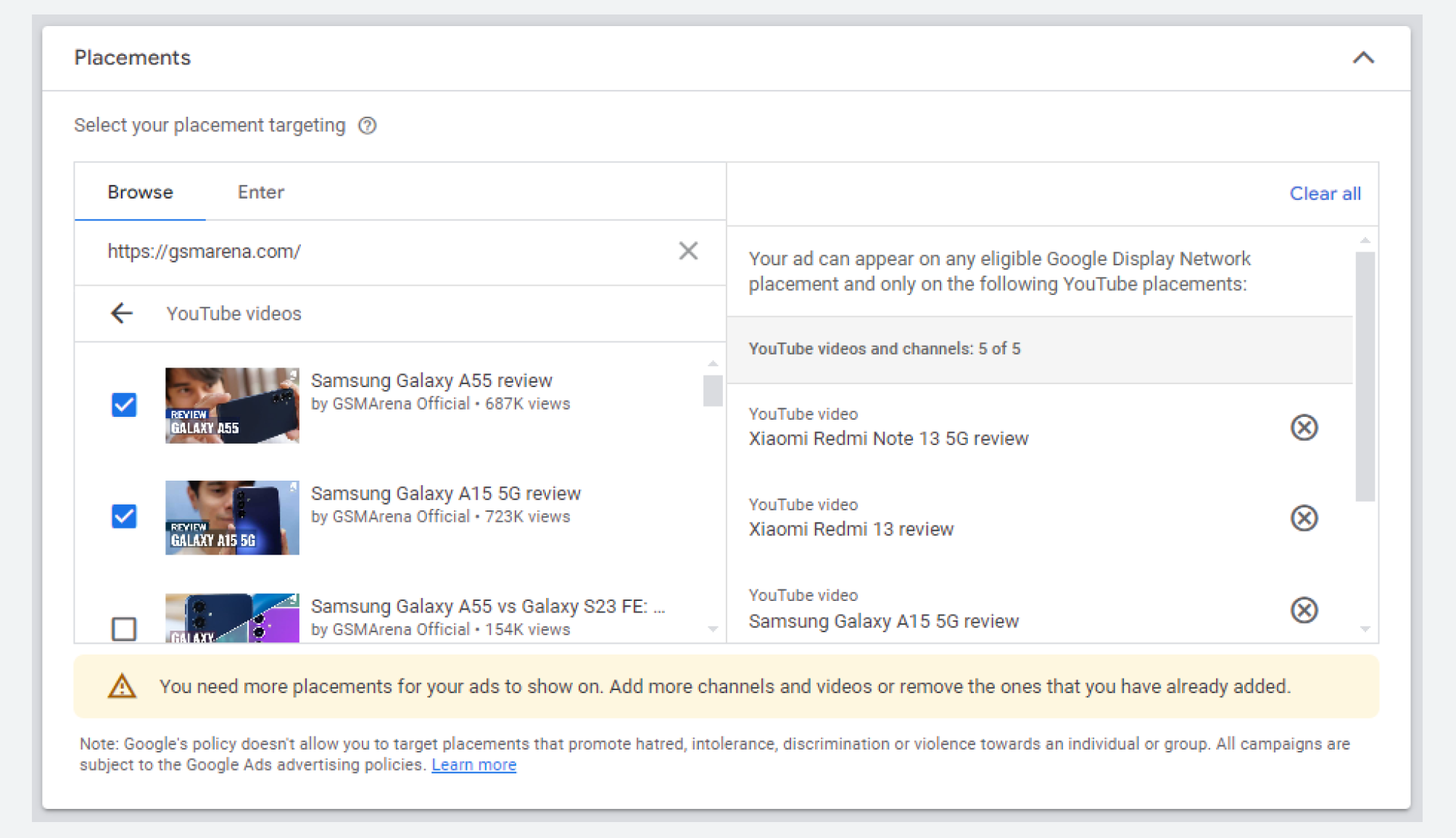
If you're running Display campaigns (especially the video ones), you can show your ads on YouTube videos related to what you're advertising.
However, finding the right placements requires careful research. Identifying the right websites or apps that attract your target audience while ensuring brand safety can be time-consuming. Besides, because you’re limiting your ads to specific placements, it may restrict your overall reach compared to broader targeting methods.
As you can see, Google lets you target specific audiences and choose where your ads appear:
- Audience targeting focuses on factors like age, gender, income, and interests to reach the right people;
- Remarketing helps reconnect with users who already know your brand, boosting your chances of making sales;
- Content targeting allows you to place ads on specific websites, apps, or topics;
- You can also target by using keywords related to your business or selecting websites that fit your brand.
Your choice will depend on how well you understand your audience and the goals you’re pursuing.
Besides these standard targeting options, there are two advanced techniques that can make your ads more effective:
Optimized targeting
Optimized Targeting (which is automatically enabled for all campaigns) uses Google’s smart algorithms to find new customers who are likely to buy your products or services. It looks at keywords on your website and in your ads to find these audiences, helping you get more sales without needing to spend more money on advertising.
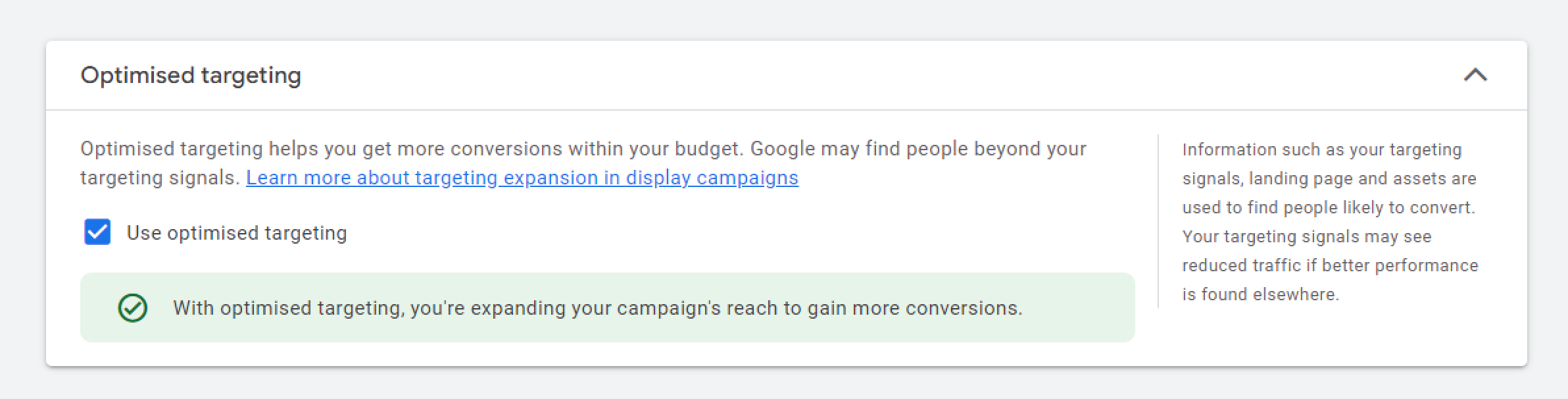
Optimized targeting is automatically enabled for all Google ads campaigns to expand your reach. If you need a more precise and narrow audience, try disabling this option.
Optimized targeting is best used when:
- You want to reach people who are very likely to buy;
- You need to find new customers beyond your current ones;
- You're looking to connect with new audiences who respond well to your ads;
- You aim to increase conversions without spending more on bids or customer acquisition costs.
You can begin with broad targeting options and turn on Optimized Targeting to let Google find the best audiences for you.
Combined segments
Combined segments let you mix different targeting criteria to create very specific audience groups. For example, you can target people who are looking to buy "athletic shoes" and are also "luxury shoppers". This helps you reach the exact people you want. You can also exclude certain groups, like people who are already your customers, to focus on finding new ones.
Here’s how you can use combined segments:
- Create detailed profiles: build profiles of your ideal customers by combining different traits, like their interests and buying behaviors. For example, if you're selling SUVs, you can target "outdoor enthusiasts" who are also "in-market for a car”;
- Layer different criteria: use various data points, like demographics and life events, to refine your audience. For example, if you sell high-end athletic shoes, target users who are actively searching for premium footwear but haven’t bought from you yet.
Experimenting here can help you find the combination of segments (i.e. targeting options) that work better for specific campaigns.
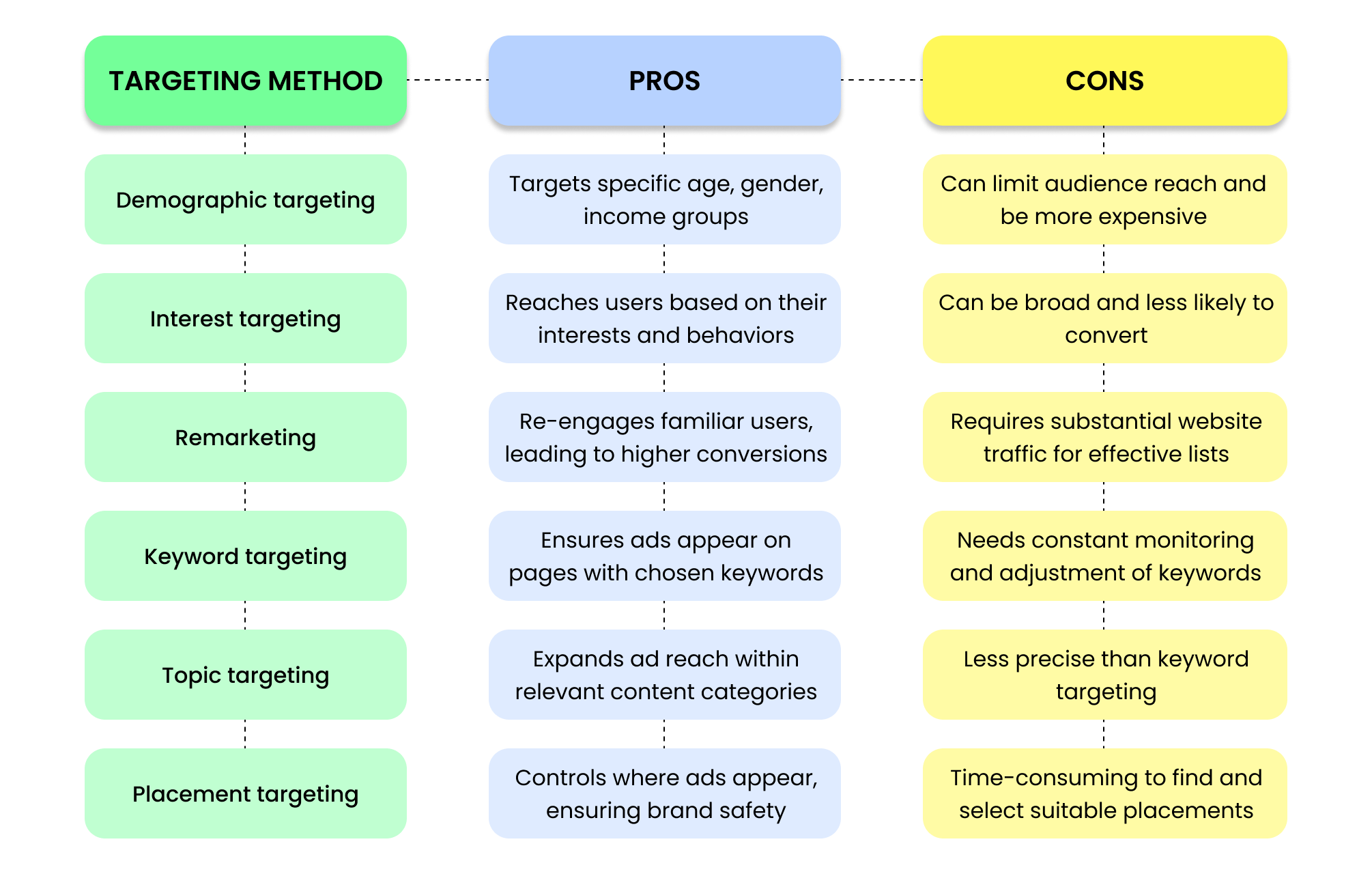
Each Google ads targeting method comes with its own pros and cons, so it's best to understand them before you make your choice.
Now, let’s consider some tips that can help you make the most of the targeting features Google provides to run profitable ad campaigns.
Best practices for Google Ads targeting
Effective targeting is crucial for optimizing your Google Ads campaigns and maximizing your return on investment (ROI). Here are key strategies to enhance your targeting efforts:
Know your target audience and segment it
Understanding your audience goes beyond basic demographics. So, dive deep into their interests, behaviors, and preferences by using tools like Google Analytics to gather insights into what drives your audience to engage with your business.
Use these insights to divide your audience into different segments, so you can create ads that speak directly to each group.
For example, you can segment your audience into groups based on their primary needs: if you sell outdoor gear, these groups can be hikers, campers, and climbers – each group needs your products for specific reasons. This way, you can create personalized ads that match each group's unique needs and interests.
Utilize targeting exclusions
To make your ad budget work better for you, it's important to exclude segments that aren’t relevant to your business. This way, you can save money and increase the chances of getting clicks and conversions from your ads.
It works like this: you can exclude specific audience types (like affinity audiences or your data segments) that don't fit with what you're advertising. This works for Search, Display, Demand Gen, and Video campaigns.
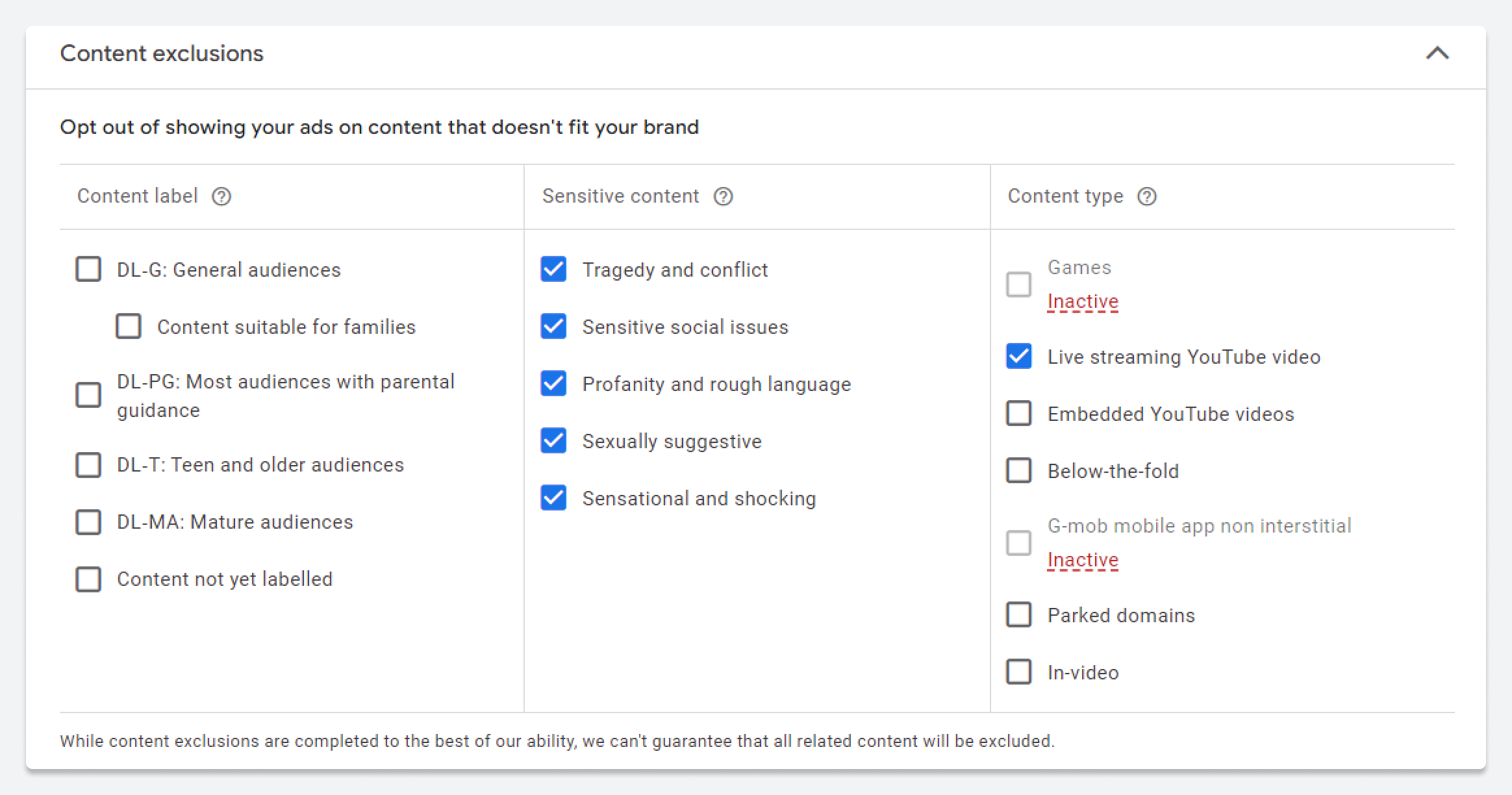
You can exclude specific types of content to avoid showing your ads in places that don't align with your brand's values or standards.
Keep in mind that while you can't add audience exclusions when you first create your campaign, you can add them later. It's a good idea to watch how your campaign performs before deciding which audiences to exclude.
You can also use content exclusion settings to avoid showing your Display ads next to content that doesn’t match your brand. By combining different exclusion types, you make sure your ads don’t appear in unwanted places.
Focus on location targeting
If your business has a physical location, using location targeting can help you connect with nearby customers who are more likely to visit your store.
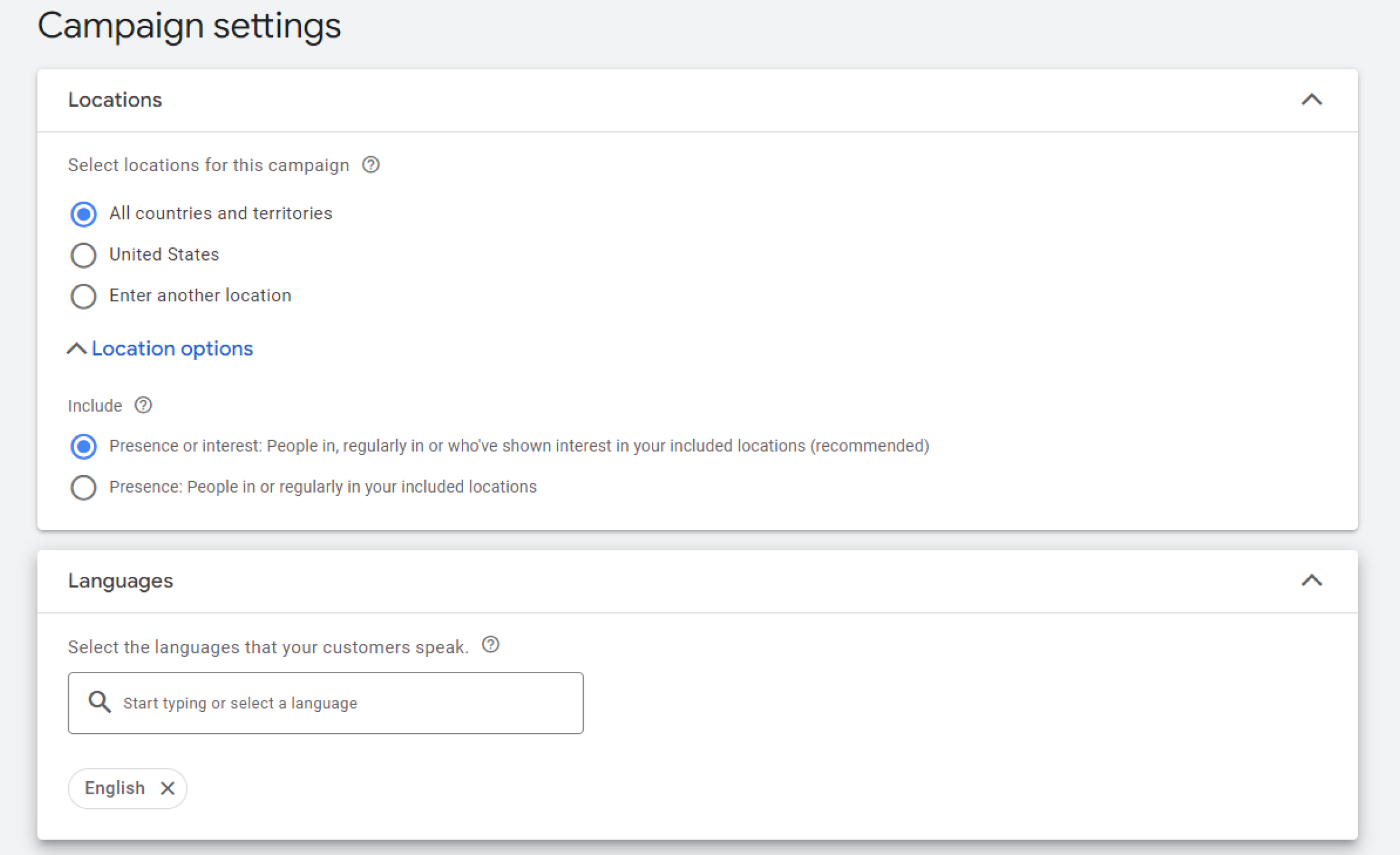
You can also set up simple location targeting right at the beginning of your campaign setup by choosing specific countries, territories, and languages.
Here’s how to do it effectively:
- Use local keywords: include keywords that mention your area specifically (e.g. “fresh pastries in Chicago”) or more generally (e.g. "fresh pastries near me”);
- Set a radius around your store: you can set a specific radius around your store to target people in the immediate area and get more foot traffic;
- Try different location settings: you can experiment with different location targeting options to see what works best. Try targeting people who are physically in your area, users who are looking for services or products in your area even if they’re not there, and so on;
- Exclude irrelevant locations: avoid spending money on areas where your business isn’t relevant by excluding them from your targeting;
- Adjust bids based on location performance: look at which areas bring the most customers and adjust your bids accordingly. If some locations perform better, increase your bids there to get more exposure;
- Customize your messaging: use geo-targeting to tailor your ads based on local preferences and cultural nuances. This makes your ads more appealing to local customers;
- Consider seasons and local events: adjust your location targeting strategy based on seasonal trends and local events. For example, if there’s a big festival in your area, you might want to target ads more aggressively to capture the increased foot traffic.
By focusing on location targeting, you can reach local customers more effectively, making your ads more relevant and increasing the chances of attracting people to your store.
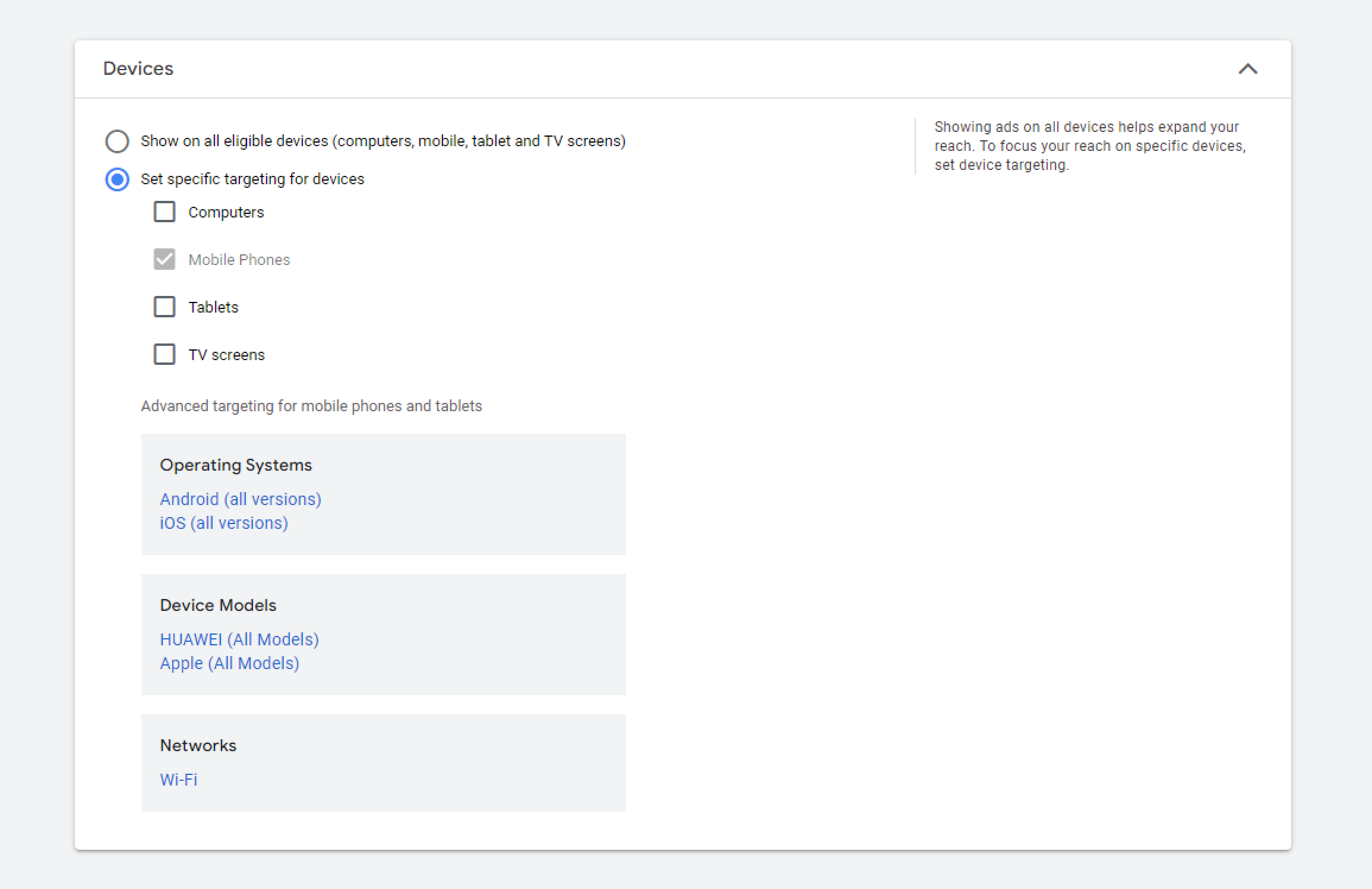
Use device targeting
As mobile device usage continues to rise, it's essential to optimize your ads for smartphones and tablets. One of the main ways to do so is to target your ads based on the devices your audience uses.
You can select specific operating systems, device models, and networks while setting up device targeting.
For this, track how your ads perform across different devices. You may find that people who use certain devices or operational system drive higher engagement and conversions. Based on these performance insights, adjust your bidding strategies accordingly: allocate more budget to devices that deliver higher conversions.
Tailor your targeting to specific types of campaigns
Each type of Google ad campaign you can run will work with specific targeting methods suited for it.
For example, Search campaigns are great for reaching users actively searching for products or services like yours on Google. To optimize targeting, select keywords relevant to your business and target in-market audiences who are currently researching or comparing similar offerings.
Display campaigns, on the other hand, focus on increasing brand awareness across Google’s Display Network. Effective targeting strategies for this campaign type include reaching affinity audiences based on long-term interests (e.g., "home decor enthusiasts") and creating custom audiences tailored to specific interests, behaviors, or demographics.
Discovery and Video campaigns (like YouTube ad campaigns) are aimed at engaging users with visually appealing content. Here, optimized targeting can be helpful: it uses Google’s machine learning to find new audiences who are likely to engage based on their browsing habits. Audience expansion can also help since your ads will reach users similar to existing customers or those who have engaged with your content.
Once you get your advertising goals clear, you’ll be able to select the type of campaign and the targeting method that fit your objectives the most.
Cost considerations for targeting your Google ads
Here’s another thing you should remember when choosing targeting methods for your Google ad campaigns: they can have different costs.
This depends on a few important factors. First, how specific and focused your target audience is plays a big role. If you're aiming at a very particular group, like high-income professionals who love luxury travel, it will often cost more per click or impression.
Secondly, the competitiveness of the keywords and audience groups you choose also matters. If lots of advertisers are bidding on the same keywords or trying to reach the same audience, it can drive up costs.
A good tip is to use Google’s Keyword Planner tool. It helps you see how competitive certain keywords are and gives you estimates on their costs. You can then adjust your bids accordingly to make sure you're getting the most out of your budget.
However, while targeted ads may have higher costs upfront, they typically generate higher conversion rates and a better ROI compared to broader, less targeted campaigns.
So, it’s important to regularly review key metrics (like CTR, conversion rate, CPA, CPC, etc.) to gauge the effectiveness of your targeting strategy, adjust bids based on that, exclude underperforming demographics or placements, and experiment with new audience segments.
This way, you can ensure that even if your targeting approach costs more initially, it brings you higher ROI that justifies the spending. To learn how to get the most out of your Google ad spend, check out our Google ad bidding guide.
Recap
In conclusion, targeting your Google Ads effectively is crucial for maximizing your advertising budget and achieving better results.
By focusing on the right audience — whether by demographics, interests, or online behavior — you increase the likelihood of reaching potential customers who are most likely to engage with your ads. This approach not only improves your conversion rates but also boosts brand awareness and allows you to refine your strategy over time based on performance data.
Also, investing in targeted ads may initially cost more but typically leads to higher returns on investment, making it a worthwhile strategy for long-term success. So, don't be afraid to experiment with different targeting strategies we've explored in this article - that's how you find what works for you.