A Guide to Google Ads Costs: Everything You Need to Know
2024-04-27

Google ads (formerly Google AdWords) is one of the most effective ways to advertise your products or services because you can target people who are actively looking for them.
However, i's reasonable to have doubts and ask yourself these questions: how much do Google ads cost? Are they worth it?
The answers depend on several factors. In this guide, we're going to explore all things related to Google ads costs: how Google ad auction works, what factors affect Google ads costs, and what you can to do lower them. Let's get started.
Are Google Ads worth it?
Google ads are like a superpower for businesses wanting to connect with their customers. They work across search engines, websites, and apps, giving businesses a chance to meet potential buyers right when they're ready to make a purchase.
If you’re doubting that, there’s quite a lot of data to prove why you should consider including Google ads in your advertising strategy.
First of all, statistics show that Google is the go-to platform for internet searches, with a global market share of over 80%. Due to such popularity and large user base, it makes perfect sense for businesses to invest in running Google ads to increase brand awareness and generate conversions. 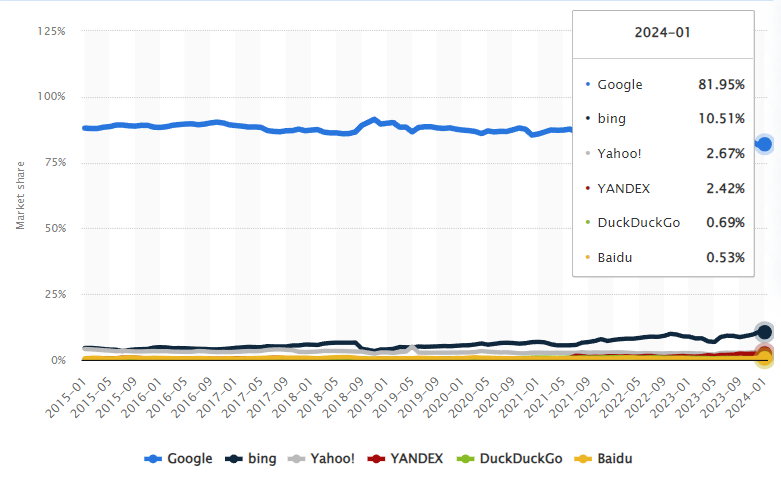
Market share of leading desktop search engines worldwide from January 2015 to January 2024. Source: Tiago Bianchi on Statista
When it comes the specific benefits you can get from running Google ads, the situation seems promising as well. For example, Databox’s research shows that a median conversion rate on Google ads is around 2.85%, which falls within the range of accepted by many advertisers as ‘optimal’ (i.e. 2-5%).
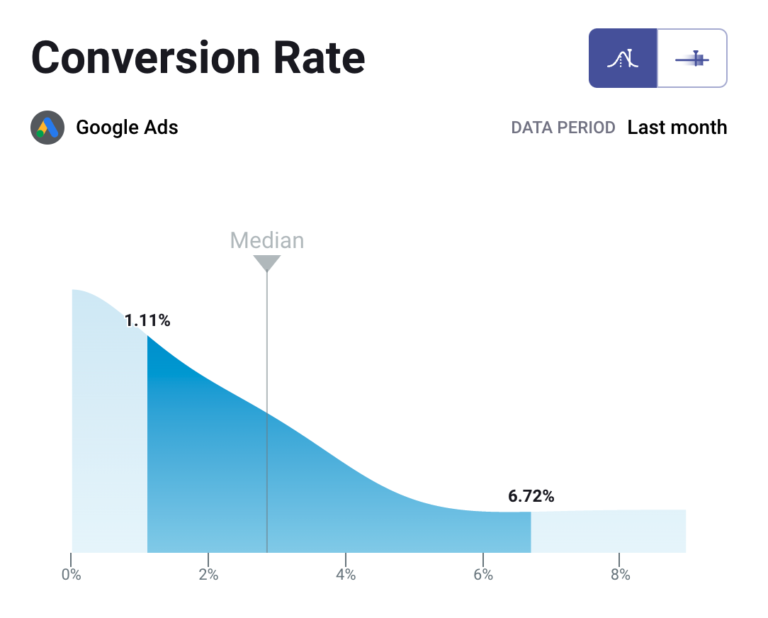
Source: Databox
As you can see, Google Ads help you make your business more visible, target the right people, and get enough conversions. But to make the most of it, you need to understand how much it costs.
Now, let’s move to the basics of how Google determines the costs of advertising.
Google ad auction: how it works
Google, like many other ad platforms, uses ad auction to determine which ads will be displayed on the search result page and where they will appear.
Here’s how the process works: when someone searches for something, Google looks at all of the ads that may be relevant to that search. Then, it takes into account several factors to determine which ads to display and in which order. The ad that wins an ad auction is displayed first. Next, the ad with the highest bid is displayed. 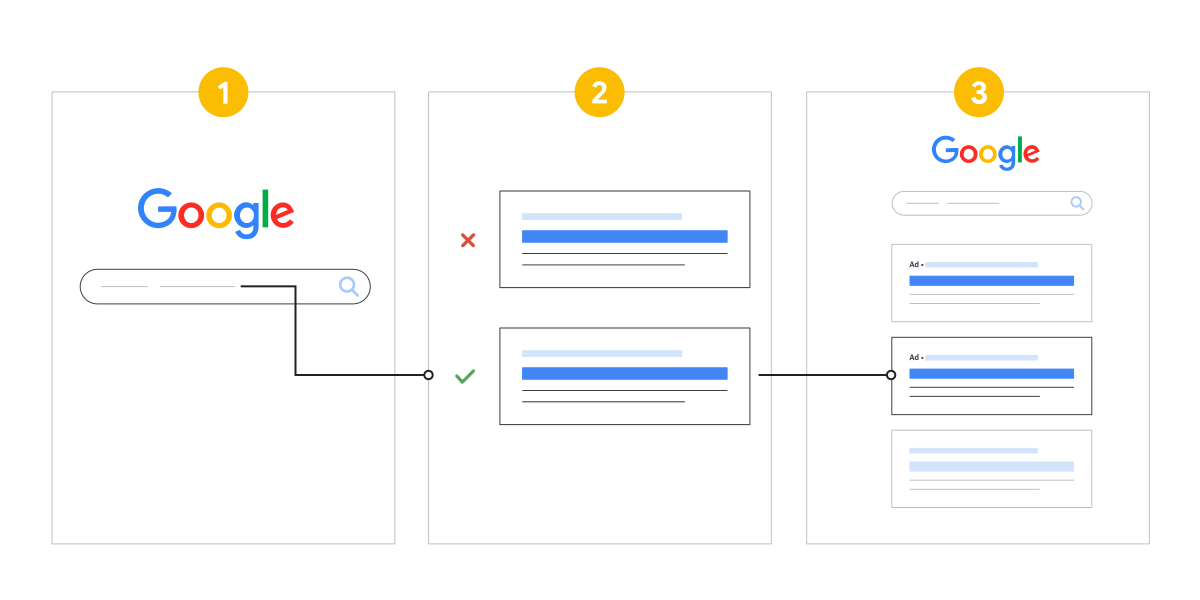
The basics of Google ad auction process. Source: Google Ads Help
Here’s what affects the ad auction outcomes:
- Ad rank, which is the threshold your ad need to reach to appear in a specific position;
- Bid amount, which indicates how much you're willing to pay for a click on your ad;
- Quality score, which reflects the quality of your ads, keywords, and landing pages;
- Ad assets, which can improve your position in search results, even if competitors bid more;
- Context, including search terms, timing, location, and device used.
Knowing how Google's ad auction works is important for running affordable and successful campaigns. It lets you make smart choices, improve your ads, and get better placements without overspending.
What affects Google ads costs?
As with ads on any other advertising platform, the costs of Google ads depend on multiple factors. Knowing them can help you answer this pressing question: why do my Google ads cost so much?
So, let’s go through them to get the full picture.
1. Industry
The main thing that affects Google ads costs is your industry.
Some industries (for example, law, finance, fitness) are more competitive and have higher CPCs, while others (like arts and entertainment) have low CPCs but must reach a much wider audience to reach their objectives. 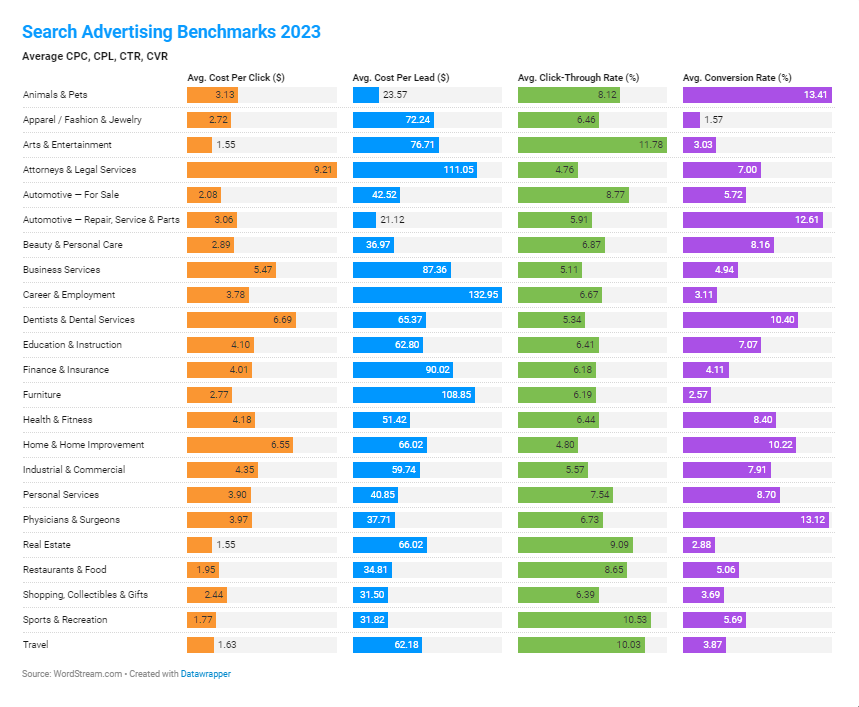
As you can see, the costs of advertising on Google can vary a lot among different industries. Source: Wordstream
In some cases, it also comes down to whether you’re focusing on consumers or other businesses as customers. For instance, a B2B company can have a lower conversion rate than a B2C company because their target market is smaller and more granular, meaning it’s less competitive.
That’s why simply comparing the CPCs and CPMs of different industries is not the best way to view the problem: while the cost per action can be quite high in your vertical, the profit you might get from each generated lead can be a lot higher than for industries with cheaper advertising costs.
In general, it’s best to check not just the costs of your Google ads, but also how cost-efficient they are, i.e. how much they bring in return for your investments. This can be achieved with a proper tracking process where you know where each conversion, call, lead form submission, etc., comes from.
In short, it’s not enough to just look at your industry’s average CPC or CPM - you also need to look at how much you can earn from your ad campaigns.
2. Keywords
Keywords are the foundation of Google advertising, and the amount you spend on your Google ads will depend on what keywords you’re using.
Here’s what matters the most when it comes to keywords:
Search volume
If a lot of people are searching for a keyword, the competition for it will be higher. The more popular a keyword is, the more advertisers are bidding on it, which drives the costs up. On the other hand, if the keywords are more specific or less popular, there may be less competition. This could result in lower costs because fewer advertisers are competing for those clicks.
Relevancy
The Quality Score is a measure of Google’s assessment of your ad’s relevance to the keyword you’re bidding on. If your ad matches the keyword and provides a positive user experience, Google will reward you with a higher quality score, which may result in lower costs.
Search intent
Last but not least, search intent of the keywords you choose also determines how effective your ads will be and thus how much you’ll pay for them. Search intent is basically the reason behind a person's online search.
Here are the main types of keyword search intent:
- Informational intent: users are searching to find information or answers to their questions. For example, "how to tie a tie" or "best restaurants in New York".
- Navigational intent: users are searching for a specific website or page. For example, "Facebook login" or "YouTube homepage".
- Transactional intent: users are looking to make a purchase or take a specific action. For example, "buy iPhone X" or "sign up for yoga classes".
- Commercial intent: users are researching products or services before making a purchase decision. For example, "best laptop for gaming" or "reviews of iPhone 12".
By aligning ad messaging and targeting with the user's intent, you can increase the likelihood of your ads being clicked and generating the results that you want.
3. Ad Rank
As we’ve mentioned earlier, your ad rank affects the results of the Google ad auction and determines where your ad will show up in the search results.
Ad Rank depends on things like how much you're willing to pay for a click (your max. CPC bid), how relevant your ad is to the keywords you’re targeting, the Quality Score, ad assets, auction’s competition, and so on. If your ad meets a certain Ad Rank level, it shows up above regular search results. But if it doesn't, it won't show at all.
Here’s the basic Google Ad Rank formula: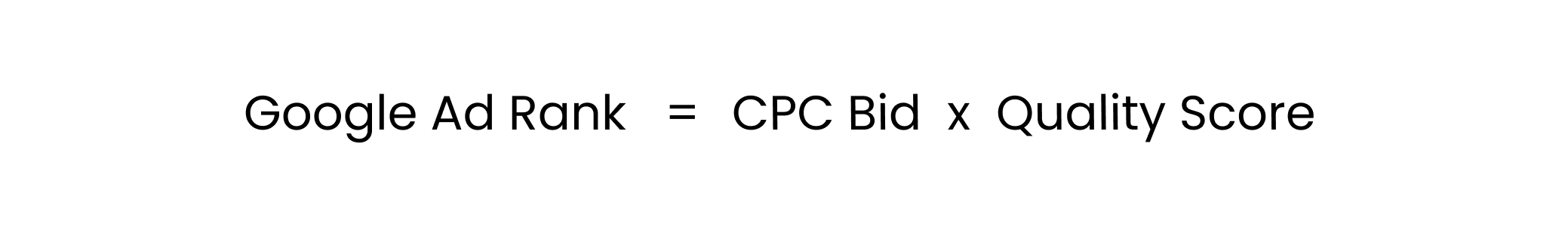
In short, the better your Ad Rank, the more likely your ad to be seen by the right people and get clicks.
But more importantly, your Ad Rank has a direct impact on the actual CPC you pay. An ad with a higher Ad Rank typically has a higher CPC per click, but it also has a higher click-through rate. Even though you’re paying more, you may see a better ROI because more people click on your ad.
An ad that appears at the top of the search results usually has a higher Ad Rank threshold, which means it can have higher CPC per click. In other words, even if there is no one below you in the search results, you may still pay more if your ad appears at the top.
But here's the thing: even though ads at the top might cost more, they often get more clicks and can show more ad assets. This means that while your ads might cost more, they’re also more likely to deliver high ROI and be cost-efficient.
4. Quality Score and ad relevancy
Quality Score is Google’s way of evaluating the quality of your ad on a scale of 1 to 10. It takes into account factors such as ad relevance to the keywords you’re bidding on, the quality of your landing page, and the expected click-through rate (CTR) of your ad.
Although Quality Score does not directly influence the ad auction results and thus ad cost, it does help you determine the ad’s relevance to specific keywords.
If your ad is more relevant than the ads of your competitors, it can take a better spot in the search results even if you don’t bid as high. On another hand, if your ads are not very relevant, you might need to spend more to compete effectively. In a way, tracking your Quality Score can help you make your ads better and spend less to get good results with them.
5. Ad formats and placements
Google ads costs can differ depending on the ad formats and ad placements you choose.
Here are the 5 types of Google ads you can run:
- Google Search ads: these show up when people search for specific keywords on Google and help you connect with users who are looking for what you offer.
- Google Display ads: these are visual banners on different websites and apps. They target users based on their interests, age, or what they're checking out online.
- Google Shopping ads: these show pictures of products along with prices and ratings. They give users a quick peek at what you're selling and can pop up in different spots on Google's search results.
- Google Video ads: these play before, during, or after videos on YouTube. They catch people's attention with visuals, sound, and stories.
- Google App ads: these are for promoting mobile apps. They can show up in lots of places, like YouTube or other apps.
Search and display ads are one of the most popular ad formats that generate a lot of clicks, which is why they might cost more.
How you set up your ad campaign and what campaign objectives you choose (e.g. traffic, sales, leads, etc.) also affects how much you’ll have to pay. It's all about finding the right balance between reaching your goals and not blowing your budget.
6. Bidding strategy
When you bid on Google Ads and enter the ad auction, you're basically saying how much you're willing to pay for someone to click on your ad or take some other action.
There are two main types of bidding on Google ads:
- Manual bidding: you set the maximum amount you're willing to pay for a click or action. This works great if you already know which keywords get you the most clicks and conversions – you can put more money into those keywords to get even better results.
- Automated bidding: basically, you let Google's algorithms do the bidding for you based on how likely your ad is to generate specific results. Within automated bidding there is also a Smart Bidding strategy that uses machine learning to set bids to get as many conversions or as higher conversion value as possible.
If you choose manual bidding, you can set a maximum bid for ad groups and keywords or a maximum CPC for specific targeting methods.
There’s also an Enhanced CPC (ECPC) strategy that allows you to benefit from manual bidding and automation at the same time: it helps you automatically adjust your manual bids for clicks that seem more likely to lead to a sale or conversion on your website. The goal of ECPC is to keep your average CPC below your target while maximizing conversions.
Automated bidding, on the other hand, includes the following strategies:
- Maximize clicks: this one's all about getting as many clicks as possible within your budget. It’s great for driving traffic to your site, but keep in mind that not all clicks are created equal and have the same profit-generating potential.
- Target impression share: this strategy pushes your ad to the top of the page for maximum visibility, but costs can vary depending on how much competition there is.
- Target CPA and Target ROAS: these two strategies focus on getting you the most conversions or conversion value with your budget based on your target metrics.
- Maximize conversions and Maximize conversion value: these strategies aim to get you as many conversions as possible or maximize the value of those conversions within your budget. You can also set a target CPA or ROAS to stay within specific limits.

Your bid, or the amount you're willing to spend for someone to click on your ad or take another action, also affects how much you pay for Google ads. You get to decide this amount based on what you can afford. However, it is important to ensure that your offer is competitive.
7. Budget
The type of ad budget you choose also affects how Google spends your money.
Here are the main budgeting options for Google ads:
- Average daily budget: this is the amount you set for each ad campaign to spend daily, giving you an idea of your monthly expenditure. For instance, you can choose to spend $10 daily on your ads.
- Daily spending limit: this is the maximum you'll be charged for a campaign in one day. It is calculated by multiplying the average daily budget by 2. For example, with a daily budget of $10, your limit could be $20.
- Monthly spending limit: this is the most you'll pay for a campaign over a month. It is calculated by multiplying the average daily budget by 30.4 (i.e. the average number of days in a month). If your average daily budget is $10, your monthly cap would be $304.
You can also set a shared budget for multiple campaigns or a total budget for video campaigns.
Keep in mind that Google optimizes your spending, focusing on days when clicks and conversions are more likely. While your spending may fluctuate day-to-day, it won't exceed your daily or monthly limits.
Even if your served costs exceed your limits in a rare case, you'll never pay more than what you've set. Here’s why: the served cost represents the total expense incurred for clicks or impressions in your campaign, whereas the billed cost reflects the amount you're accountable for after adjustments, like deductions for invalid activity, have been applied to your account. This means that your billed cost will always stay within your spending limits.
8. Target audience
The cost of your Google ads can also depend on who you're trying to reach. If you’re competing for the same group of users with many other advertisers, you’ll have to spend more to get to the search top.
There are also other factors besides the audience popularity that may affect the ad costs:
- Audience size: high competition can happen with both broad and specific audiences, which means that there’s no universal solution when it comes to finding cheaper targeting options. More than likely, you’ll have to experiment with several audiences to find the best fit in terms of costs and ad relevancy.
- Audience behavior: some audience segments are more likely to actively interact with ads than others, which can affect the way Google views your ads (i.e. as more or less relevant). Audience behavior heavily depends on their intent: users who are ready to convert are more likely to be interested in an ad that offers specific products or services, while users looking to compare different options will pay more attention to organic results rather than paid ads.
- Devices: how your audience accesses Google Search can also play a role in how expensive your ads will be. For example, advertisers have a better chance to reach customers on their mobile devices and do it at cheaper costs because way more people use their phones to Google things. Desktop traffic tends to be lower than mobile, which potentially means higher advertising costs.
Understanding your target audience and how they behave online can help you manage your advertising costs on Google.
9. Ad schedule
As with any other platform, timing of your Google ads plays a huge role when it comes to advertising costs: they can vary significantly based on the time of year, the day of the week, time of day.
When people are active online, ads generally cost more due to increased competition. During periods of lower activity, on another hand, ads tend to be cheaper as there are fewer advertisers fighting for ad space. If you know when your ads get more clicks or impressions, you can use dayparting, i.e. set the ad schedule for your Google ads to pick the best hours or days to reach potential customers. This way, you can spend more of your budget on busy times when more people are online and decrease the ad spend during slow hours.
Ad scheduling also allows you to target time-specific keywords, for example, terms like “restaurants open now” to show your ads to people who look where to dine late in the evening, and so on. This provides a lot of opportunities for local businesses looking to find more customers.
To sum up, knowing all the variables that can affect your Google ads costs is definitely a must if you want to be fully prepared to meet any challenges that might come your way.
How much should you spend on Google ads?
When you're putting money into Google Ads, it's not just going out into the vast unknown: you're targeting specific markets, each with its own costs and factors to think about. And when you bid for clicks or website visitors on Google, you're competing for the ones that matter to your business and, logically, to your competitors.
But how much does it actually cost to advertise on Google, and how much should you spend to get good results? While there's technically no minimum spend on Google Ads, you won’t get too far with a daily budget of $2-$5. As Google operates based on an ad auction system, the more you’re willing to pay, the more valuable your ad will be from Google’s POV.
The optimal Google ads spend amount also depends on your skills: if you’re experienced in setting and optimizing ad campaigns, you can consider starting with a bigger budget. If you’re a newbie, it’s best to start with a budget that won’t break the bank but will still be competitive enough.
Here’s how you can calculate how much you need to spend in the beginning:
- Check the average cost per click (CPC) for your industry;
- Set the goal for a day, e.g. getting 10 clicks;
- Multiply the number of clicks you want to get each day by the average CPC.
Following this algorithm, you’ll get a minimum amount of money to spend on your Google ads daily. Keep in mind that spending more money means you can get more clicks and more data about what works and what doesn’t – this is essential for further optimization and scaling. However, you don’t want to waste your budget only to get nothing substantial in return. That’s why it’s crucial to understand what strategies you can use to reduce your Google ads CPC or CPM while still getting enough valuable data from running ads.
6 strategies to lower Google ads costs
1. Select the right keywords
As mentioned earlier, keywords are crucial for Google Ads. It's important to pick the right ones if you want to keep your ads relevant and profitable.
Here are some tips to do so:
Use more specific keywords
The less keywords you use for your ads, the more likely it is that you’ll have to pay more for each click. Essentially, targeting just one or two search terms leads to a higher competition with other advertisers for the same audience and thus higher costs.
That's why it might be smarter to choose more keywords, especially the long-tailed ones. Long-tail keywords, or more specific phrases, can be useful because they're less competitive and are often more relevant and cost-efficient. Even though they may not get as much traffic, they can potentially bring more conversions, which means you can end up spending less on your ads and still reach potential customers.
You can use Google Keyword Planner to find keywords and see how often they're searched for. Look for keywords that are relevant and likely to lead to conversions based on their search volume, CPC, and the volume change over time.
Try different keyword match types
Google offers different match types for keywords: broad, phrase, and exact. Each of them controls how closely your keyword needs to match a user's search query for your ad to show up.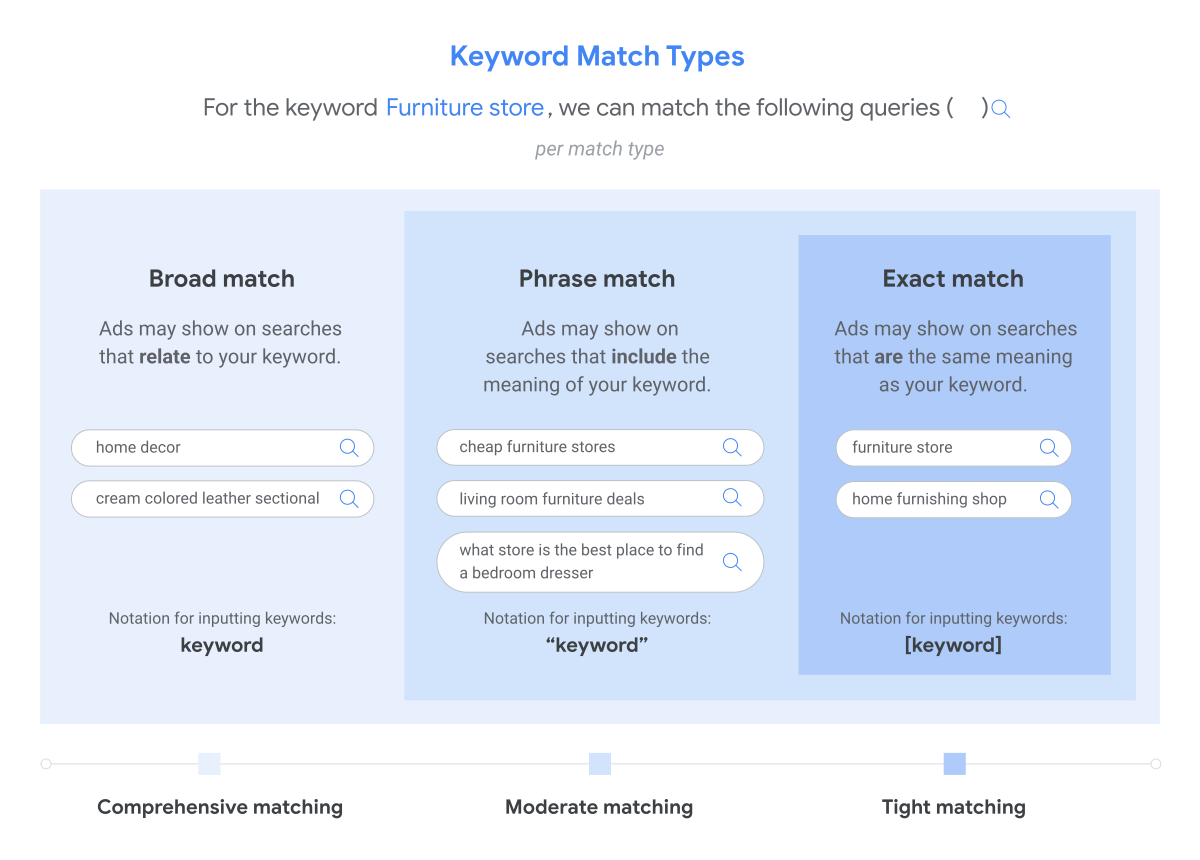
Different types of keyword match available on Google. Source: Google Ads Help
Broad match can lead to more impressions but may also attract less relevant clicks. Phrase match and exact match are more targeted and can help ensure your ads are shown to people actively looking for what you offer. By using match types strategically, you can improve the relevance of your ads and reduce wasted ad spend on irrelevant clicks.
Use negative keywords
To stop your ads from showing up for terms that aren't related to your business, create a list of negative keywords to exclude them from your campaigns.
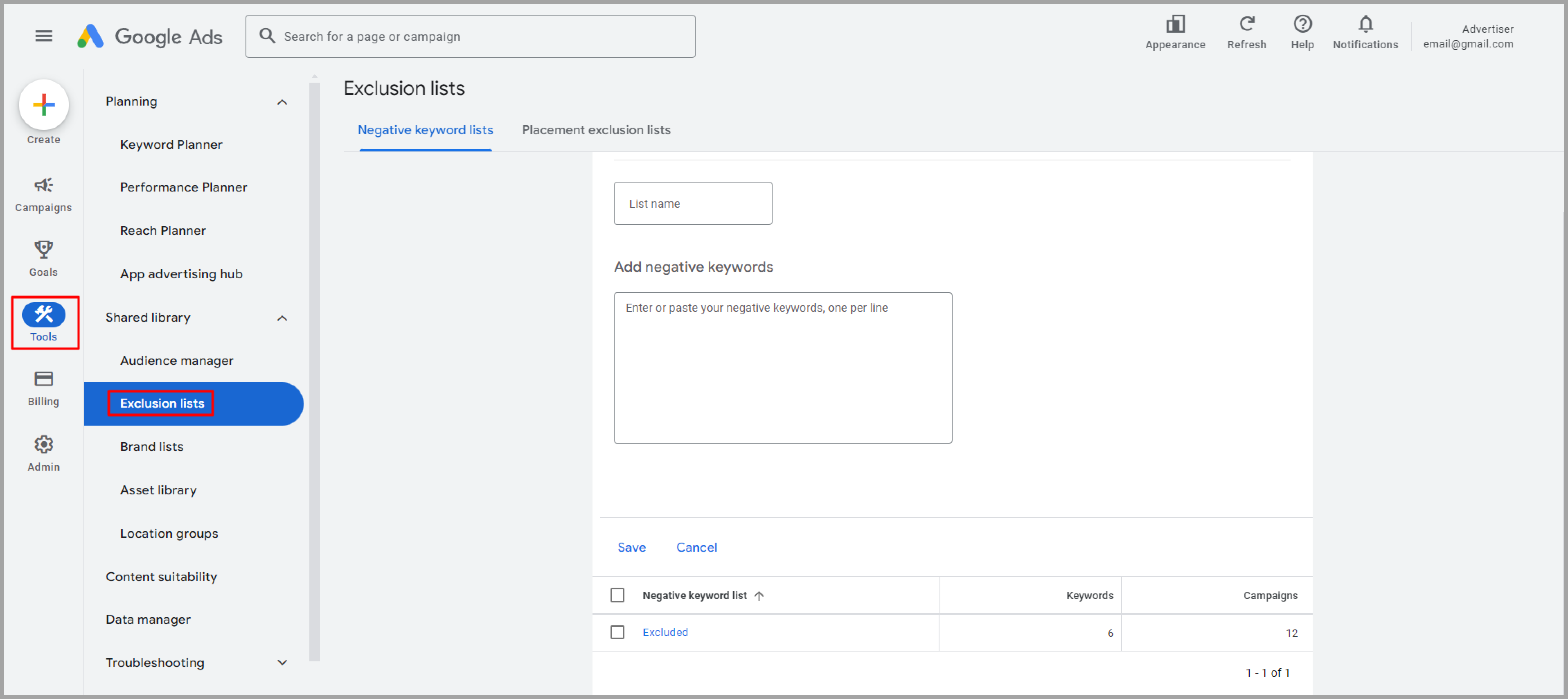
You can add multiple negative keyword lists as well as exclude certain placements.
For example, if you sell high-end products, you might exclude terms like "cheap" or "free" to make sure your ads are shown to the right people. The more relevant your ads are, the better results they’ll deliver and the lower their costs will be.
Choose keywords with buying intent
Focusing on keywords relevant for people who are ready to make a purchase (like "buy", "order", or "best deals") can make it a bit easier to get conversions and a good ROI. Also, remember to check how your keywords are performing. This way, you can keep the ones that are working well and get rid of the ones that aren't.
2. Target relevant audiences
Choosing the right audience to target for your Google ads can help you not only get better results from them but also run them at cheaper costs. But to pick the right option, you need to know exactly who you want to see your ads.
Here are the audiences you can target on Google:
- Affinity segments based on interests and habits;
- Custom segments which can be based on keywords that show certain interests, or websites or apps they might be interested in. You can also create your own target groups (i.e. custom audiences) based on data from your website, app, or customer records;
- Detailed demographics, or targeting based on age, gender, household income, and parental status;
- Life events – targeting based on life milestones (moving, marriage, job change, graduation, starting a business, retiring, etc.);
- In-market, ortargeting based on people’s recent purchase intent.
Since what people's needs constantly change, it's smart to try out different targeting methods and see which ones work best. Here are a few tactics you can try to lower your advertising costs:
Device targeting
You can choose to show your ads only on certain devices, like mobile or desktop. If you know your audience mostly uses smartphones to search on Google, you can try targeting mobile users only. This way, won’t be wasting your ad budget showing ads on devices your audience doesn't use much.
Targeting by devices can provide the following benefits:
- Cost efficiency: you can focus your budget targeting the devices your audience uses the most, avoiding spending money on options that don't drive as many conversions.
- Optimized user experience: tailoring your ads to particular devices allows you to provide better user experience and optimize your landing pages for specific audiences, increasing the likelihood of engagement and conversions.
- Flexibility: adjusting bids and ad messaging based on devices can help you develop a more flexible and responsive advertising strategy.
Keep in mind that you can use Google Analytics to check how your audience uses different devices to access your website before deciding which ones to target in your Google ad campaigns. This way, you can focus your ad budget on something that actually works.
Geo targeting
If you’re advertising a local business or segment your audience into several groups based on whether they’re from, you can target users from specific locations. This not only helps you avoid spending money showing ads to people who aren't likely to become customers but also allows you to make your ads more relevant and personalized for each audience segment.
Here’s why you might want to choose location targeting:
- Higher ad relevancy: targeting specific locations ensures that your ads are seen by people in areas where your business operates or where your primary target audience is located.
- Cost savings: by avoiding showing your ads to irrelevant or geographically distant audiences, you can save money and improve your ROI.
- Local optimization: localized ads can help drive foot traffic to physical stores or local events, maximizing the impact of your advertising efforts. Don’t forget that you can always use ad assets to provide more relevant information about your business (e.g. exact location, ratings from local review platforms, etc.).
Demographic targeting
Targeting based on age, gender, or parental status is the basic way to specify the audience that might be interested in your offers and avoid spending money showing ads to people who aren't.
Here’s why demographic targeting can be useful for you:
- Higher ad relevancy: tailoring ads based on demographic factors ensures that your messaging resonates with the intended audience, increasing engagement and conversions.
- Personalization: demographic targeting creates opportunities for personalized ad experiences, making users feel understood and valued, which can lead to stronger brand loyalty.
- Improved CTR and conversion rate: by optimizing ads for specific demographic segments, you can improve overall ad performance and get a better ROI.
Income targeting
Besides the usual demographic characteristics, Google also allows you to target people based on their household income level. If your product or service is aimed at high-income earners, you can focus your ads on them. This way, you're not wasting money showing ads to people who might not be able to afford what you're offering.
Targeting by income allows you to get these perks:
- Qualified leads only: using income targeting helps you ensure that your ads are seen by people who are more likely to afford your products or services, increasing the likelihood of conversions.
- Higher ROI: by focusing your budget on high-income earners, you can avoid wasting resources on audiences less likely to convert, leading to better cost efficiency.
- Tailored ads: income targeting allows you to segment your audience into several groups and develop tailored messaging and offers that resonate with specific income demographics.
Retargeting
Running retargeting campaigns based on different types of data allows you to show your ads to people who have already visited your website or interacted with your business in some way, i.e. to warm audiences. Since these people already know about your products or services, they're more likely to become customers – you just have to give them the right incentive.
Here’s why retargeting should be a part of your Google ad strategy:
- More conversions: retargeting allows you to re-engage with users who have already shown interest in your brand or products, increasing the likelihood of conversion.
- Higher brand recall: keeping your brand top-of-mind with retargeting ads ensures that users remember your brand even after leaving your website, leading to higher brand recall and recognition.
- Cost-efficiency: retargeting often results in lower ad costs compared to targeting cold audiences, as you're advertising to users who are already familiar with your brand and more likely to convert.
3. Experiment with bidding strategies
When you're setting up your ads on Google, you'll decide how much money to spend each day for each campaign. Keep in mind that you might not end up spending all of it. Besides, you can control your spending better by keeping separate budgets for each campaign.
When it comes to bidding strategies, it's important to choose the right maximum CPC bid – this is the highest price you're willing to pay for someone to click on your ad. The higher your bid, the better your ad might perform. So, even though higher bids can mean higher costs, you might see better results in the end.
Google also provides AI-based bidding features that figure out the best bids for your ads based on what you want to achieve. For example, you can use Smart Bidding to optimize for conversions or conversion value and reach a certain CPA or ROAS.
4. Use ad assets
Google ad assets are the parts of your ad that provide additional information about your business. They can include things like headlines, descriptions, links to parts of your website, buttons to call your business, location info, and so on.
Google decides which extra parts of your ad to show based on what someone searches for, and with the right ad assets you can cover all possible needs when it comes to the information a potential customer might need. If you add useful links and relevant images to your ad, it will stand out from all the rest among the paid search results and get a higher CTR.
Depending on the type of ad asset, Google might add it automatically if it thinks it will improve your ad's performance, or you’ll need to set it up manually. The good news is that it doesn’t cost anything to add ad assets, so you can benefit from prodiving relevant information to your audience without paying more.
5. Improve Quality Score
As we’ve stated before, Google will rank your ad based on its quality and relevance. Ads that are considered irrelevant or poorly written will end up costing more, so it makes sense to try and increase the Quality Score to make your ads more cost-efficient.
If you follow the previous strategies, you’ll improve your ads' Quality Scores as a result as you’ll make them relevant for specific keywords, optimize your langing pages for faster speed and better user experience, write ad copies that make people want to click, use ad assets to provide additional information, and so on.
If your ad is spot-on and meets people's needs, Google will see it as more relevant and you'll likely pay less for clicks. If you're uncertain, check out ads of your competitors on Google Ads Transparency Centre to see how good they are – this can help you find winning strategies to use in your own campaigns.
6. Set up conversion tracking
If you don’t know where your conversions come from, it will be difficult to accurately analyze how cost-efficient your ads are. That’s why it’s crucial to track your conversions properly when you're running Google ads.
Here are the steps you’ll need to take for conversion tracking:
- Pick the specific actions you want to track that match your campaign goals;
- Choose the best way to track them, like using Google's conversion tag or other tools depending on what you're tracking;
- Keep an eye on the data and use what you learn to make your campaigns better.
Once your conversion tracking is all set up, you’ll see the data about conversions in your Google ads dashboard. This includes things like how often people are converting, how much each conversion costs you, and more. You can compare this data with what's typical in your industry to see how well your ads are doing.
Recap
Keeping your Google ads costs low while getting good results involves understanding many different things that affect how much you spend. From choosing the right keywords to setting budgets and analyzing competition, there's a lot to consider.
Deciding how much money to put into Google Ads depends on what you want to achieve, who you're targeting, and how competitive your industry is. With careful planning, proper analysis, and tried and tested strategies, you can make the most of your Google Ads budget and reach your advertising goals effectively.

